Variables:
Variables can be considered as the name of a container. In other words, a variable is a container whose value can change depending on certain conditions.
When we allocate a value to a variable, it is known as a variable assignment.
In python, the syntax for it is variable_name = value
My birthday
1
st July
5:00 PM
12/2, Rajouri Gardens
9898463123
Now depending on whose birthday it is and who is being
invited, the details being filled in the ‘_______’ (blank space)
keep on changing…right?
Imagine this ‘________’ as a container and the details being filled
are the values. This value can change depending on
circumstances.
Variables can be considered as the name of a container. So in the
above example,
date=”1
st July”
address=”12/2, Rajouri Gardens”
If the card is filled by someone else it can be,
date=”21
st July”
address=”34, MG road”
Here, date, address, etc are containers (variables), and “1
st July”,
”12/2, ``Rajouri Gardens”, “21
st July” etc are values.
Rules for forming Python variables:
● A variable name must start with a letter or the underscore character.
● A variable name cannot start with a number.
● A variable name can only contain alpha-numeric characters and underscores (A-z, 0-9, and _ )(space is not allowed)
● Variable names are case-sensitive (age, Age, and AGE are three different variables)
Datatype:
Datatype is the type of value assigned to a variable. Depending on values that are assigned to a variable, a few common data types (variable type) in python are
suppose you want to take a printout of a birthday card.
What details do you have to enter into the
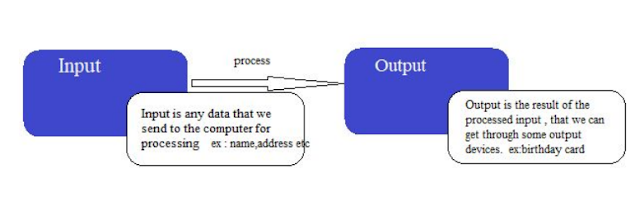
computer, each time you take a printout? all the variables(like name, address, etc) have to be entered. And once you enter the variables, you will get the birthday card printed …right? So the variable data you enter is known as the input and the birthday card you get is the output.
computer, each time you take a printout? all the variables(like name, address, etc) have to be entered. And once you enter the variables, you will get the birthday card printed …right? So the variable data you enter is known as the input and the birthday card you get is the output.
Output in python
print () ->prints message given between () with newline(default)
Note :
● “” is used with strings/ messages
● If we give “” for the variable it will be considered as a string.
● By default terminating the character of the print, the statement is a newline.
Input in python
● input()
● When the input() function executes program flow will be
stopped until the user has given input.
● By default, all input in python is taken as a string.
Syntax
Input(
program to get the name of the birthday boy from the user.
In both the above versions, the name is the variable that holds the
child’s name as a value.
Program to Get all the relevant details from users and prepare a birthday invitation card.
Program to Get all the relevant details as input and make a birthday invitation
card
Get the invitee address details from the user and print out an address slip
to be pasted on the invitation card.
Output:












Comments
Post a Comment